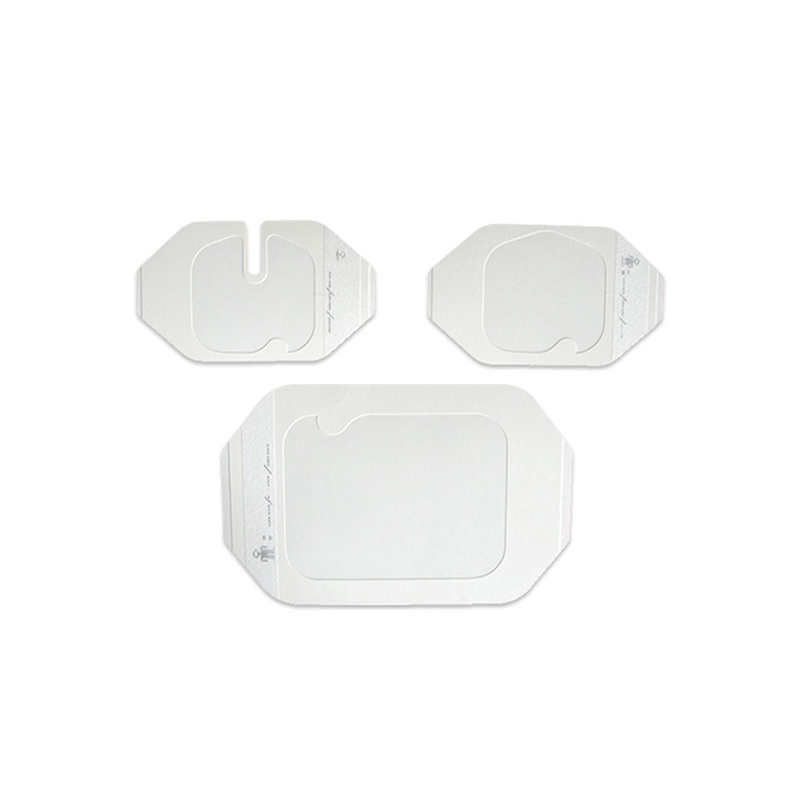
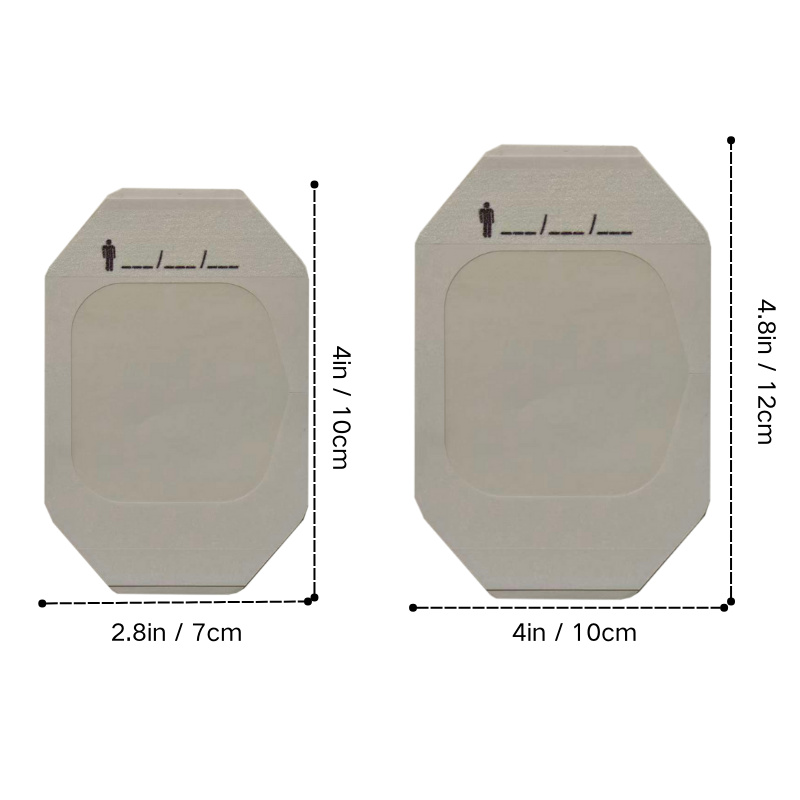
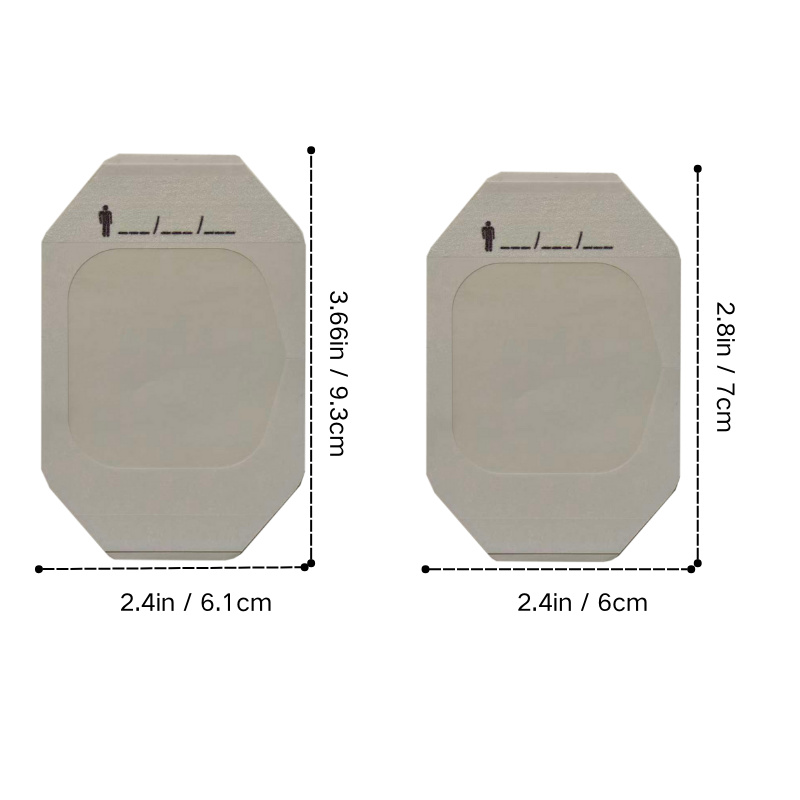
Main functions of I.V. Dressing
Prevent infection: The intravenous injection or catheter insertion point is exposed to the external environment and is susceptible to the invasion of bacteria and contaminants. Especially when the patient needs intravenous injection or continuous infusion for a long time, the use of I.V. Dressing can effectively avoid these sources of contamination and prevent the occurrence of infection. By using sterile breathable materials, the dressing can seal the puncture point while ensuring that the environment around the wound remains clean.
Keep dry: I.V. Dressing uses breathable materials to allow air to enter the wound area through the dressing, helping to keep the wound dry. If the wound is kept moist for a long time, it may cause skin softening, infection or other complications. I.V. Dressing with good breathability helps maintain a moderate moist environment, promotes wound healing and prevents excessive moisture.
Provide comfortable protection: I.V. Dressing is designed with patient comfort in mind. It is usually made of soft materials, which can effectively reduce the friction of patients around the injection or catheter insertion point. In addition, its adhesive layer is usually low in irritation, which can reduce damage to sensitive skin and is particularly suitable for long-term wear.
Reduce complications: For patients who need long-term infusion, I.V. Dressing can help stabilize the intravenous catheter and reduce the risk of catheter displacement or dislocation, thereby reducing complications caused by improper catheter insertion. In addition, by regularly replacing I.V. Dressing, problems caused by venous puncture, such as thrombosis and phlebitis, can be reduced.
Easy to monitor and care: Many I.V. Dressings are transparent, allowing medical staff to directly observe the puncture site without changing the dressing. This design not only improves the efficiency of care and reduces secondary interference with the wound, but also can promptly detect abnormalities at the puncture site, such as redness, swelling or exudation, and adjust the treatment plan in time.
What are the main materials of I.V. Dressing?
The materials and designs of I.V. Dressing are highly professional, mainly through its multi-layer material structure to achieve wound protection, comfort and breathability, while ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the medical process. Each layer of material is carefully designed to meet the high standards for dressings during intravenous injections, catheter management and other medical treatments. The following is a detailed analysis and function of each layer of material:
Outer layer material: The outer layer is usually made of waterproof and breathable materials such as polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane film. Its main function is to prevent external contaminants (such as bacteria, dust and liquid) from entering the dressing while effectively maintaining air circulation. This layer of material can prevent liquid penetration, thereby keeping the puncture site dry and preventing moisture accumulation and infection. In addition, the breathable design ensures that the wound can "breathe", which is crucial for wound healing, because lack of oxygen or moisture retention will delay the healing process and may increase the occurrence of complications.
The outer layer material needs to have a certain degree of flexibility and stretchability to adapt to the changes of the skin, especially when the patient is active or wears it for a long time, to ensure that it is not easy to tear or loose. In addition, the waterproofness of the outer layer material can also protect the puncture site from the invasion of sweat or water vapor, thereby enhancing the protection of the wound.
Adhesion layer: The adhesion layer is a vital part of I.V. Dressing, usually using non-irritating, hypoallergenic medical glue, acrylic glue and other materials. These materials adhere firmly to the patient's skin without causing excessive pressure or discomfort to the skin. Their main function is to firmly fix the dressing to the puncture site and prevent the dressing from loosening or falling off due to the patient's daily activities or friction.
To ensure the comfort of the patient, the adhesive layer needs to have appropriate adhesion. It must ensure firm adhesion without excessive irritation to the skin, especially for patients with sensitive skin. In addition, the adhesive layer should be designed to ensure that it will not cause damage to the skin when removed, avoid adhesion damage to the skin, and reduce secondary damage to the skin.
Breathable layer: The breathable layer is usually made of soft and elastic materials. It is a very important layer in I.V. Dressing and plays a role in ensuring the exchange of air between the wound and the outside world. The design of this layer of material ensures that air can smoothly pass through the dressing into the wound area, thereby maintaining a proper moist environment for the wound and reducing the risk of excessive moisture accumulation. By maintaining a moderately moist environment, the breathable layer helps promote the regeneration of skin cells and the rapid healing of wounds.
The breathable layer is not only required to have good breathability, but also needs to be soft and elastic to adapt to the expansion and movement of the skin. This is especially important for patients who wear it for a long time or move more, because the breathable layer can avoid skin discomfort and wound irritation caused by friction. The breathable layer with good elasticity can also stretch appropriately with the changes of the skin, ensuring that the dressing can fit the skin tightly without wrinkles or gaps, thereby preventing bacterial invasion.
Synergy of multi-layer structure: The multi-layer structure of I.V. Dressing combines multiple functions such as waterproof, breathable, and adhesive to ensure the efficiency and comfort of the dressing during use. Each layer of material complements each other during use and plays a different protective role:
The outer layer of material provides a barrier to prevent the invasion of external pollutants while ensuring breathability;
The adhesive layer ensures that the I.V. Dressing can fit the skin firmly and is not easy to fall off;
The breathable layer promotes healing and reduces the risk of infection by maintaining a moist environment for the wound.
This multi-layer structure design makes I.V. Dressing not just a simple dressing, but a sophisticated medical tool that ensures the comfort of patients during treatment while minimizing health risks caused by wound infection, moisture accumulation, foreign body invasion, etc.
Application scope of I.V. Dressing
The application scope of I.V. Dressing is very wide, mainly focusing on scenarios where treatment requires intravenous injection, catheter management and long-term treatment during medical procedures. The following are detailed applications of I.V. Dressing in several major areas:
Intravenous infusion: During intravenous injection and infusion, the main function of I.V. Dressing is to protect the puncture point and prevent the invasion of external bacteria, dust and other contaminants. Intravenous injection is a common treatment method, especially in antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy, nutritional supplementation and other treatments that require intravenous infusion. I.V. Dressing can provide a closed protective environment for the puncture point to prevent bacteria from entering, while keeping the wound dry and clean, thereby effectively reducing the risk of infection and improving treatment safety, which is especially important in patients with weak immune systems. In addition, I.V. Dressing can also reduce the irritation caused by external friction or pressure at the injection site, ensure the stability of the injection process, avoid frequent dressing changes, reduce damage to the skin, and fully protect the injection site.
Catheter management: For patients who need to use intravenous catheters for a long time, I.V. Dressing plays a vital role in catheter management. Intravenous catheters are often used for chemotherapy, long-term nutritional support (such as enteral nutrition) for tumor patients, and treatment of patients with chronic diseases. Since the catheter is inserted into the blood vessel, long-term use is prone to infection or catheter displacement affecting the treatment effect. I.V. Dressing can firmly fix the catheter, reduce its position change and fall off, and ensure that the catheter remains stable during treatment. Through stable adhesion, it effectively reduces the friction of the catheter and prevents secondary trauma or infection caused by unstable fixation. At the same time, I.V. Dressing isolates the contact between the catheter and the external environment and reduces the impact of external pollution sources on the catheter area. In patients who wear catheters for a long time, I.V. Dressing can also reduce skin discomfort caused by catheters. The breathable material ensures that the skin breathes normally, reduces moisture retention, and prevents skin damage and infection, thereby providing higher comfort and better treatment effects.
Long-term treatment: I.V. Dressing is not only suitable for short-term injections or catheter use, but is also more suitable for patients who need long-term treatment, especially patients with diabetes, chronic diseases or cancer, who usually need frequent intravenous treatment. During long-term treatment, patients may face the challenge of frequent drug changes and long-term injections. The multi-layer design of I.V. Dressing can provide continuous protection for the treatment site, effectively prevent local infection, keep it dry and clean, and help patients maintain a high quality of life. It can also reduce irritation and discomfort at the injection site, improve comfort, and avoid the inconvenience caused by frequent dressing changes. For patients who use catheters for a long time, I.V. Dressing can stably fix the catheter and prevent the risk of catheter displacement or detachment. In addition, the breathable design of I.V. Dressing helps reduce skin damage, keep the wound surface dry, prevent skin softening and ulcer formation, and ensure that patients get better comfort and results during treatment.